Unlocking Rheumatoid Arthritis: Navigating Google for Essential Health Information
Navigating the complexities of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) can be daunting, but understanding how to effectively use search engines like Google to find reliable health information is crucial. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation of the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and potential damage. Early diagnosis and intensive treatment are vital to prevent long-term joint damage and improve quality of life for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Many people experiencing persistent joint pain or morning stiffness are searching for answers, and recognizing the early symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis is the first step towards getting appropriate care. Exploring resources that offer comprehensive insights on Rheumatoid Arthritis management can provide immense support and clarity, ensuring patients are well-informed about their condition and available treatments. Understanding the progression of rheumatoid arthritis, from initial symptoms to advanced stages, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare journey, highlighting the importance of accurate and accessible health information.
A person researching rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and treatments on a laptop, surrounded by medical diagrams.
Demystifying Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comprehensive Overview for Healthcare Professionals
Rheumatoid arthritis presents a significant challenge for healthcare professionals due to its systemic nature and varied clinical manifestations. It's an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. This attack leads to inflammation, causing significant pain, swelling, and stiffness in the affected joints. Over time, this chronic inflammation can erode cartilage and bone, leading to joint deformity and functional impairment. Proper diagnosis requires a thorough understanding of the symptoms, serological markers, and imaging findings. For instance, differentiating rheumatoid arthritis from other forms of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, is crucial for effective treatment strategies. Professionals often refer to detailed medical guidelines and research papers to stay updated on the latest advancements. Exploring resources that provide innovative approaches to medical and pharmaceutical services can offer new perspectives on managing chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, benefiting both practitioners and patients alike.

A group of medical professionals discussing a patient's chart, focusing on rheumatoid arthritis diagnostic criteria.
Crucial Topics to Master for Conquering Arthritis: Your Definitive Guide
To effectively conquer rheumatoid arthritis, individuals must master several crucial topics, ranging from understanding the disease's mechanisms to implementing effective self-care strategies. Recognizing the early symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, such as persistent joint pain, swelling, and morning stiffness, is paramount for timely intervention. Awareness of the role of the immune system in this autoimmune disease helps in comprehending why certain treatments are prescribed. Furthermore, patients need to grasp the importance of adherence to medication regimens, including DMARDs, to control inflammation and prevent joint damage. Understanding how to manage flares, those periods of increased disease activity, is also a vital skill for long-term health. Learning about lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, and how they impact inflammation can significantly improve outcomes. For those seeking personal growth alongside health management, discovering resources that help learn how to manifest with the law of attraction can provide mental and emotional resilience, which is often crucial in managing chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
An illustrative guide depicting various strategies for managing rheumatoid arthritis, including medication, exercise, and diet.
Why Understanding RA Management and Treatment is Paramount for Adults with Arthritis
For adults living with rheumatoid arthritis, a deep understanding of RA management and treatment is not merely beneficial; it's paramount for maintaining quality of life and preventing irreversible joint damage. Rheumatoid arthritis can severely impact daily activities, causing persistent pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in affected joints. Effective treatments aim to reduce inflammation, alleviate symptoms, prevent damage to joints, and achieve remission. This includes a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. Neglecting early symptoms or inadequate treatment can lead to progressive damage, deformity, and disability. Understanding the nuances of DMARDs and biologics, their potential side effects, and how they interact with the body's immune system is crucial for informed decision-making. Consulting with a rheumatologist is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific challenges of one's rheumatoid arthritis. Engaging with a healthcare provider who understands the intricacies of this autoimmune disease is critical. Discovering reliable providers who offer expert legal advice for healthcare matters can be important for patients navigating their treatment journey and rights.

A healthcare provider explaining different rheumatoid arthritis treatment options to an adult patient during a consultation.
Historical Context of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Tracing the Autoimmune Disease
The historical understanding of rheumatoid arthritis reveals a journey from mysterious debilitating illness to a recognized autoimmune disease with specific treatment protocols. Early descriptions of symptoms resembling rheumatoid arthritis can be found in ancient texts, but it wasn't until the 19th century that it was clearly distinguished from other forms of arthritis like gout and osteoarthritis. The term "rheumatoid arthritis" was coined by Dr. Alfred Baring Garrod in 1859. For centuries, treatments were largely palliative, focusing on symptom relief rather than disease modification. The discovery of corticosteroids in the mid-20th century marked a significant turning point, providing effective, albeit temporary, relief from inflammation. Subsequent advancements led to the development of Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) and later, biologics, revolutionizing the prognosis for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Understanding this historical progression underscores the continuous efforts to combat the devastating effects of rheumatoid arthritis and improve patients' lives. As with any historical research, ensuring access to resources that guarantee meticulous data organization and maintenance is key to accurate and comprehensive studies.

A timeline depicting key historical milestones in the understanding and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Current Landscape of Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatments: An Information Deep Dive
The current landscape of rheumatoid arthritis treatments is characterized by a multi-faceted approach aimed at suppressing the immune system's inflammatory response, alleviating pain, and preserving joint function. Modern treatments for rheumatoid arthritis typically involve a combination of Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs), which include conventional synthetic DMARDs (e.g., methotrexate), targeted synthetic DMARDs (e.g., JAK inhibitors), and biologic DMARDs (e.g., TNF inhibitors). These treatments work to slow disease progression and prevent irreversible joint damage. The goal is to achieve remission or low disease activity, minimizing pain and inflammation. While these treatments have significantly improved outcomes, they can also come with potential side effects, necessitating careful monitoring by a healthcare provider. Patients often need to weigh the benefits against the risks in consultation with their rheumatologist. Advancements in pharmacotherapy continue to emerge, offering new hope for those with challenging rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. It's crucial for patients and practitioners to be informed about the latest research and treatment guidelines to optimize care. For home comfort that complements a healthy living environment, understanding reliable expert heating system installation and maintenance is often considered an essential part of maintaining overall well-being.

An infographic illustrating the different classes of medications used in current rheumatoid arthritis treatments and their mechanisms of action.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Management and Treatment: Proven Strategies for Joint Function
Effective management of rheumatoid arthritis goes beyond medication, encompassing a holistic approach to preserve joint function and enhance quality of life. Proven strategies integrate various therapeutic modalities to tackle the chronic inflammation and pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Physical therapy plays a crucial role, with tailored exercises designed to maintain joint flexibility, strengthen surrounding muscles, and improve overall mobility. Occupational therapy helps individuals adapt to daily tasks, minimizing stress on affected joints. Pain management techniques, including hot and cold therapies, assistive devices, and sometimes even complementary approaches, are vital for alleviating discomfort. Lifestyle modifications, such as regular, low-impact exercise and a balanced, anti-inflammatory diet, can also significantly contribute to managing symptoms and reducing inflammation. The aim is to create a comprehensive plan that empowers individuals to actively participate in their own care, ensuring the best possible outcomes for their joints. This proactive approach helps in mitigating long-term damage and preserving joint integrity.
A patient performing gentle exercises with a physical therapist, illustrating effective rheumatoid arthritis joint management strategies.
Crucial Topics to Master for Conquering Arthritis: Your Definitive Guide
The initial steps in diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis are critical and often begin with recognizing key signs and symptoms that differentiate it from other musculoskeletal conditions. Patients typically present with persistent joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, particularly in the small joints of the hands and feet, often in a symmetrical pattern. Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes is a hallmark symptom. Other constitutional symptoms might include fatigue, low-grade fever, and unexplained weight loss. A thorough medical history, physical examination assessing all joints for tenderness and swelling, and blood tests are essential. These tests often look for inflammatory markers like CRP and ESR, as well as specific autoantibodies such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies. Early diagnosis is crucial because rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that can lead to irreversible joint damage if not treated promptly.
A doctor examining a patient's hands, specifically checking for swelling and tenderness in the joints, during a rheumatoid arthritis diagnostic consultation.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Genetic Factors and Autoimmune Disease
Understanding rheumatoid arthritis involves appreciating the complex interplay of genetic factors and its classification as an autoimmune disease. While not purely hereditary, a predisposition to rheumatoid arthritis can be passed down through families, with certain genes, particularly variants of the HLA-DRB1 gene, significantly increasing risk. These genetic factors influence the immune system’s response, making it more likely to mistakenly attack the body's own tissues, specifically the synovium in the joints. However, genetics alone do not determine who develops rheumatoid arthritis; environmental triggers such as smoking and certain infections are also thought to play a crucial role in initiating the autoimmune response in genetically susceptible individuals. This intricate relationship between genetic susceptibility and environmental factors highlights why rheumatoid arthritis is considered a multifactorial autoimmune condition, contributing to the varied presentation and progression of the disease among different patients. The complex nature of this autoimmune disorder demands a comprehensive diagnostic approach.
A diagram illustrating the genetic and environmental factors contributing to the development of rheumatoid arthritis.
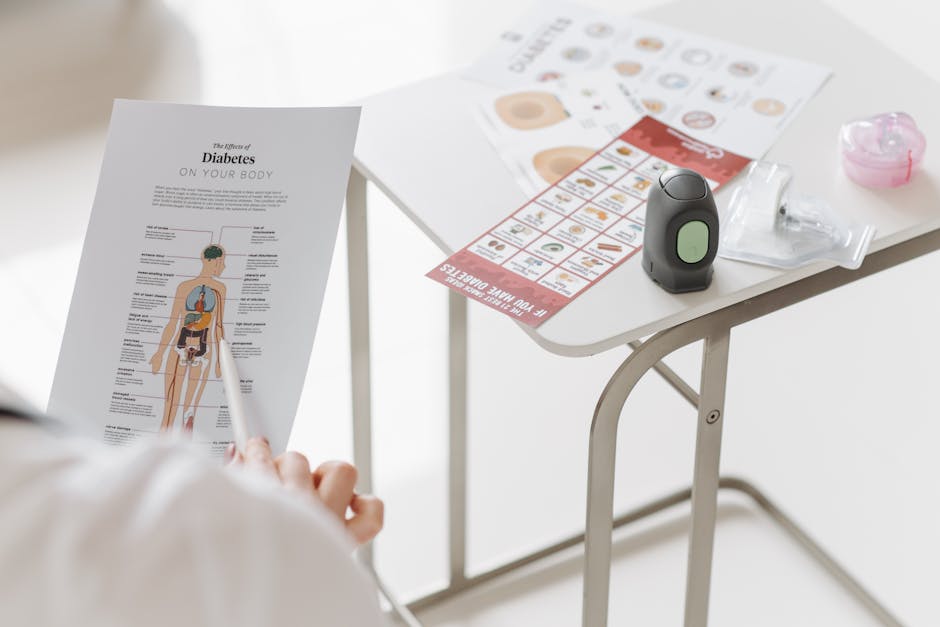
Essential Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis Stages and Constitutional Symptoms
Grasping the stages of rheumatoid arthritis and its constitutional symptoms is essential for both patients and healthcare providers to manage the disease effectively. Rheumatoid arthritis typically progresses through four stages: early, moderate, severe, and end-stage. The early stage involves mild joint inflammation with some pain and stiffness, often without visible damage. As the disease advances to the moderate stage, cartilage erosion and narrowing of joint space become evident, leading to increased pain and stiffness. The severe stage is marked by significant joint damage, deformity, and potential loss of function. The end-stage can involve complete joint fusion and extensive damage to other organs. Beyond localized joint issues, constitutional symptoms such as persistent fatigue, low-grade fever, loss of appetite, and general malaise are common throughout these stages, reflecting the systemic nature of rheumatoid arthritis and the ongoing immune system activity.

A four-panel illustration depicting the progression of rheumatoid arthritis through its distinct stages, from early inflammation to severe joint damage.
Why Understanding RA Management and Treatment is Paramount for Adults with Arthritis
A comprehensive analysis of rheumatoid arthritis encompasses the entire spectrum of the disease, from the challenging periods of flares to the coveted state of remission. Flares are acute episodes of increased disease activity, characterized by intensified joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, often accompanied by heightened fatigue and constitutional symptoms. Managing flares effectively involves prompt intervention, sometimes requiring adjustments in medication or short courses of corticosteroids. The ultimate goal of rheumatoid arthritis treatments is to achieve remission, a state where disease activity is minimal or absent, significantly reducing inflammation and preventing further joint damage. Achieving and maintaining remission is crucial for preserving joint function and improving long-term quality of life, though it often requires ongoing vigilance and adherence to a treatment plan. Understanding the triggers for flares and strategies for managing them is just as important as working towards sustained remission.
A graph showing the fluctuating course of rheumatoid arthritis, illustrating periods of flares and remission over time.
Critical Elements in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment: Disease-modifying Agents
Critical elements in rheumatoid arthritis treatment revolve around the strategic use of disease-modifying agents, which are foundational to controlling the disease’s progression. These agents, primarily Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs), work by modifying the immune system’s response to reduce inflammation and prevent joint damage. Unlike simple pain relievers, DMARDs target the underlying autoimmune processes. Conventional synthetic DMARDs, such as methotrexate, sulfasalazine, and hydroxychloroquine, are often the first line of treatment. Their effectiveness lies in their ability to suppress the overactive immune system, thereby mitigating the destructive effects of rheumatoid arthritis on the joints. The early initiation of DMARD therapy is strongly emphasized to halt the progression of joint damage and achieve better long-term outcomes for individuals suffering from persistent pain and inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis.
An illustration of various DMARDs, showcasing their chemical structures and how they interact with the immune system to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Tailored Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Disease-modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs
Tailored treatments for rheumatoid arthritis often center on Disease-modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs), customized to individual patient profiles and disease severity. Beyond conventional synthetic DMARDs, biological DMARDs (biologics) and targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs) have revolutionized treatment options. Biologics, such as TNF inhibitors or IL-6 inhibitors, are engineered proteins that specifically target components of the immune system involved in inflammation. tsDMARDs, like JAK inhibitors, block specific pathways within immune cells. The choice of DMARD is influenced by factors such as disease activity, previous treatment responses, comorbidities, and patient preferences. A personalized approach ensures that patients receive the most effective treatment with the fewest adverse effects, optimizing their chances of achieving remission and maintaining joint function. The ongoing development of new DMARDs continues to expand the therapeutic arsenal against rheumatoid arthritis, offering hope for improved outcomes for those with this chronic autoimmune condition.

A medical chart highlighting different DMARD options and patient-specific factors influencing treatment decisions for rheumatoid arthritis.
Historical Context of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Tracing the Autoimmune Disease
The second major topic delves into advanced clinical tools and comprehensive education essential for managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively. This includes leveraging sophisticated imaging techniques like MRI and ultrasound to detect early joint damage and monitor disease progression, which are more sensitive than traditional X-rays in identifying subtle changes in the joints. Beyond diagnostics, advanced clinical tools extend to patient monitoring systems, allowing healthcare providers to track disease activity, treatment adherence, and potential side effects in real-time. Educational initiatives are equally vital, empowering patients with in-depth knowledge about their condition, self-management strategies, and the importance of active participation in their care plan. These tools and educational resources collectively contribute to a more personalized and proactive approach to managing rheumatoid arthritis, aiming to minimize the impact of the disease on daily life and long-term health outcomes.
A screenshot of a clinical dashboard displaying patient data, disease activity scores, and treatment adherence for rheumatoid arthritis management.
Implementing Effective Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing effective rheumatoid arthritis treatment options requires a structured, step-by-step approach, beginning with a definitive diagnosis and culminating in a tailored, ongoing management plan. The first step involves a comprehensive assessment by a rheumatologist, confirming rheumatoid arthritis and evaluating disease severity. Next, the selection of appropriate Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) is made, often starting with methotrexate unless contraindications exist. Regular monitoring follows, involving clinical assessments, blood tests, and imaging, to evaluate treatment efficacy and detect any adverse effects. Adjustments to medication or the addition of biological agents are made based on the patient's response and disease activity. Patient education on medication use, potential side effects, and self-care strategies is continuously provided. This iterative process ensures that treatments remain optimized to control inflammation, alleviate pain, and prevent joint damage, leading to improved outcomes for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
A flowchart depicting the step-by-step process of implementing rheumatoid arthritis treatment, from diagnosis to ongoing management.
Step-by-Step Process for Initiating Rheumatoid Arthritis Medication
Initiating rheumatoid arthritis medication follows a systematic step-by-step process designed to optimize efficacy and minimize risks. Initially, after diagnosis, the rheumatologist will discuss various medication options, typically starting with a conventional synthetic DMARD like methotrexate, as it is often highly effective in controlling inflammation and slowing disease progression. Patients receive detailed instructions on dosage, administration (oral or injectable), and potential side effects. Baseline blood tests are conducted to check liver and kidney function, and these tests are regularly repeated to monitor for adverse effects. Education about the expected timeline for medication effectiveness and the importance of adherence is crucial. If the initial medication is not adequately controlling symptoms after a few months, the rheumatologist will consider dose adjustments, combination therapy with other DMARDs, or switching to a biologic drug. This methodical approach ensures that the treatment for rheumatoid arthritis is carefully managed and adjusted as needed, adapting to the individual patient's response and disease activity.
A medical professional explaining the initial steps of a methotrexate regimen to a patient newly diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, with a medication bottle visible.
Current Landscape of Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatments: An Information Deep Dive
Beyond conventional treatments, advanced techniques in rheumatoid arthritis management are constantly evolving, offering new avenues for improving patient outcomes. These cutting-edge approaches often involve targeted therapies that precisely modulate the immune system, such as novel small molecules and advanced biological agents that address specific inflammatory pathways. Gene therapy and stem cell research are also emerging areas with significant potential, aiming to repair damaged tissues and re-regulate the immune system at a fundamental level. Furthermore, personalized medicine, guided by genetic profiling and biomarker analysis, allows for highly tailored treatment plans, predicting individual responses to therapies and minimizing adverse effects. These advanced techniques represent a significant leap forward, providing hope for better disease control, reduced pain and inflammation, and enhanced joint function for those living with persistent rheumatoid arthritis, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in autoimmune disease management.
Microscopic view of immune cells and targeted drug molecules, representing advanced rheumatoid arthritis treatment techniques.
Expert Tips for Optimal Joint Function in Rheumatoid Arthritis Adults
For adults living with rheumatoid arthritis, maintaining optimal joint function is paramount, and expert tips often focus on a combination of lifestyle adjustments and proactive care. Regular, low-impact exercise such as swimming, cycling, or walking helps preserve joint flexibility and strengthen surrounding muscles without exacerbating inflammation or pain. Incorporating ergonomic principles into daily activities, such as using assistive devices or modifying tasks, can reduce stress on affected joints. Prioritizing rest during flares and ensuring adequate sleep are crucial for managing fatigue and allowing the body to recover. A balanced, anti-inflammatory diet, rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, can also help reduce systemic inflammation. Regular communication with a rheumatologist, physical therapist, and occupational therapist ensures that treatment plans are continuously optimized and adapted to changing needs, supporting long-term joint health and overall well-being despite the challenges of rheumatoid arthritis.
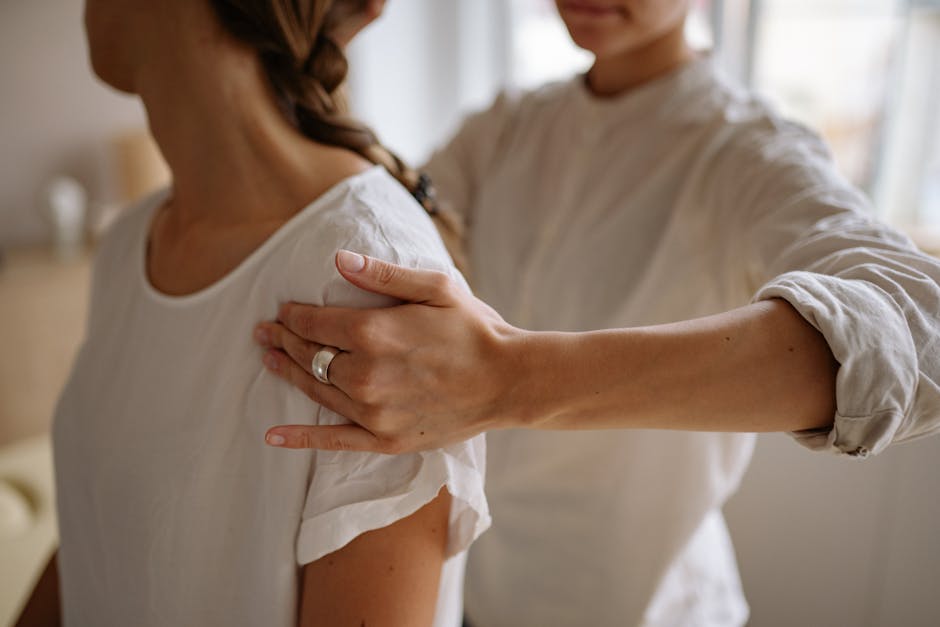
An adult with rheumatoid arthritis performing gentle hand exercises to improve joint flexibility, guided by a healthcare professional.
Cutting-edge Rheumatoid Arthritis Research: Hydrogen Therapy and Its Potential
Cutting-edge rheumatoid arthritis research is exploring novel therapeutic avenues, with hydrogen therapy emerging as a promising area of investigation. While still in its early stages, studies suggest that molecular hydrogen, a powerful antioxidant, may have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects that could benefit individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Research indicates that hydrogen can selectively neutralize harmful free radicals, reduce oxidative stress, and downregulate inflammatory cytokines, thereby potentially alleviating pain, swelling, and inflammation in affected joints. This non-pharmacological approach offers the prospect of a complementary or alternative therapy that could reduce the reliance on conventional medications or enhance their efficacy, with fewer side effects. Although more extensive clinical trials are needed to confirm its long-term benefits and safety, hydrogen therapy represents an exciting frontier in the quest for more effective and less invasive treatments for rheumatoid arthritis, offering new hope for symptom management.

A conceptual image of hydrogen molecules interacting with inflammatory cells in a joint, symbolizing the potential of hydrogen therapy for rheumatoid arthritis.
Third Major Topic: Future of Rheumatoid Arthritis Research and Guidelines
The third major topic delves into the dynamic future of rheumatoid arthritis research and the evolving guidelines that will shape patient care. Research is increasingly focused on precision medicine, aiming to identify specific biomarkers that can predict disease activity, treatment response, and potential for remission, thus allowing for highly individualized therapeutic strategies. Advances in genetic sequencing and proteomics are uncovering new insights into the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, paving the way for novel drug targets. Furthermore, the development of biosimilars is expanding access to effective biologic treatments, making them more affordable globally. Future guidelines will likely emphasize earlier intervention, more aggressive treatment to achieve sustained remission, and comprehensive care that addresses comorbidities. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in analyzing vast datasets will also accelerate discovery and refine treatment protocols, promising a future where rheumatoid arthritis is not just managed, but potentially cured.

A visual representation of a research lab setting, with scientists collaborating on future rheumatoid arthritis treatments and diagnostic tools.
Transformative Rheumatoid Arthritis Case Studies: Success Stories from Mayo Clinic
Transformative rheumatoid arthritis case studies, particularly those from esteemed institutions like the Mayo Clinic, offer invaluable insights into effective management and treatment strategies. These success stories highlight patients who have achieved significant remission or improved quality of life despite severe or refractory rheumatoid arthritis. They often showcase the power of interdisciplinary care, combining the expertise of rheumatologists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and even mental health professionals. These case studies frequently detail complex diagnostic challenges, the journey through various treatment modalities—from conventional DMARDs to cutting-edge biologics—and the impact of personalized treatment plans. They serve as powerful examples of how early diagnosis, aggressive treatment, patient adherence, and innovative approaches can dramatically alter the trajectory of rheumatoid arthritis, emphasizing the potential for positive outcomes even in challenging circumstances and providing hope for those living with the disease.
A collage of patient testimonials and medical charts from Mayo Clinic, illustrating successful rheumatoid arthritis treatment outcomes.
Key Lessons Learned from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient Journeys and Prognosis
Key lessons learned from the diverse journeys of rheumatoid arthritis patients significantly inform prognosis and future care strategies. One overarching lesson is the critical importance of early diagnosis and prompt, aggressive treatment to prevent irreversible joint damage and maintain functional independence. Another vital insight is the variability of disease progression, underscoring the need for highly individualized treatment plans that adapt to each patient’s unique response and challenges, including flares. Patients’ experiences also emphasize the profound impact of rheumatoid arthritis beyond physical symptoms, affecting mental health, social interactions, and overall well-being. Therefore, a holistic approach that includes psychological support and patient education is crucial. These journeys highlight that while there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, effective management can lead to remission and a significantly improved quality of life, empowering patients to live full and active lives.

An illustration showing a patient's journey with rheumatoid arthritis, emphasizing turning points in treatment and quality of life improvements.
First Steps in Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis: Identifying Key Signs and Symptoms
The future trends in rheumatoid arthritis point towards a landscape of increasingly sophisticated and personalized treatment options, aiming for better outcomes and ultimately, a cure. Emerging developments include a focus on preventative strategies, identifying individuals at high risk before the onset of clinical symptoms and intervening proactively. There is a strong prediction for growth in biomarker-guided therapies, where specific molecular markers in a patient's blood or tissue dictate the most effective treatment pathway. Advances in regenerative medicine, such as innovative stem cell therapies and tissue engineering, hold promise for repairing damaged joints and restoring function. Furthermore, the integration of digital health technologies, including wearables and AI-powered diagnostics, will enhance monitoring and enable more precise, real-time adjustments to treatment plans. These trends collectively paint a picture of a future where rheumatoid arthritis management is more precise, less invasive, and more effective in achieving sustained remission for a wider range of patients.

A futuristic medical interface displaying genomic data and personalized treatment recommendations for rheumatoid arthritis.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Genetic Factors and Autoimmune Disease
Emerging developments in rheumatoid arthritis treatments and associated products & services are rapidly transforming patient care, offering new hope and improved quality of life. Pharmaceutical innovation continues to introduce novel small molecules and advanced biologics with improved specificity and safety profiles, targeting previously unaddressed inflammatory pathways. Beyond medication, there's a growing market for complementary products and services, including specialized physical therapy tools, ergonomic aids, and nutritional supplements designed to support joint health and reduce inflammation. Digital health platforms are also emerging, providing remote monitoring, virtual consultations, and educational resources tailored for rheumatoid arthritis patients. These developments collectively enhance the comprehensive care model, empowering patients to better manage their condition, minimize pain and stiffness, and maintain an active lifestyle. The focus is increasingly on a personalized approach, integrating these diverse developments to optimize individual treatment plans and improve overall outcomes for those living with rheumatoid arthritis.
An array of innovative products and services for rheumatoid arthritis management, including ergonomic tools and digital health apps.
Essential Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis Stages and Constitutional Symptoms
Google plays an undeniably pivotal role in disseminating health information about rheumatoid arthritis, making it crucial for users to navigate search results discerningly to avoid incorrect information. While Google provides immediate access to a vast array of resources, from medical journals to patient forums, the challenge lies in distinguishing credible sources from misinformation. Organizations like the Arthritis Foundation, NIH, and Mayo Clinic offer reliable, evidence-based content. Users should prioritize websites with .gov, .edu, or well-known medical institution domains, and always cross-reference information from multiple reputable sources. Google's algorithms strive to rank high-quality content, but critical evaluation skills remain essential. Understanding common symptoms, the nature of this autoimmune disease, and available treatments through verified channels empowers patients to make informed decisions and engage constructively with their healthcare providers, ensuring they receive accurate health information and appropriate care for their rheumatoid arthritis.
A search engine results page with various links related to rheumatoid arthritis, highlighting trusted medical sources versus less reliable ones.
Charting Your Course: Definitive Next Steps for Conquering Arthritis and Optimizing Health Information
Charting your course towards conquering rheumatoid arthritis involves definitive next steps focused on optimizing health information and active participation in your care. Once diagnosed, the immediate priority is to work closely with a rheumatologist to establish a personalized treatment plan that targets inflammation and prevents joint damage. This plan will likely include Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs), regular monitoring, and lifestyle modifications. Simultaneously, empower yourself by continuously seeking high-quality, evidence-based health information from reputable sources to understand your condition, treatment options, and self-management strategies. Engage with support groups and patient advocacy organizations for emotional support and shared experiences. Remember, effective management of rheumatoid arthritis is a marathon, not a sprint, requiring ongoing commitment and collaboration with your healthcare team. Proactive engagement with your health information ensures that you remain an informed and empowered partner in your journey to conquer arthritis.
A compass overlaid on a medical chart, symbolizing the definitive next steps in managing rheumatoid arthritis and optimizing health information.
Why Understanding RA Management and Treatment is Paramount for Adults with Arthritis
In concise summary, rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease primarily affecting the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness, particularly in the hands and feet. Key symptoms often include morning stiffness lasting over 30 minutes, symmetrical joint involvement, and constitutional symptoms like fatigue. Diagnosis hinges on a comprehensive assessment involving medical history, physical examination for swollen joints, blood tests (e.g., RF, anti-CCP, ESR, CRP), and imaging studies. Treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis are focused on controlling inflammation, alleviating pain, and preventing joint damage, predominantly through the use of Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs), including conventional synthetic, targeted synthetic, and biologic agents. Physical therapy and lifestyle modifications complement medication to optimize joint function and improve overall quality of life. Early intervention and a personalized treatment approach are critical for managing this complex condition and mitigating its long-term impact on the body's joints.
An infographic summarizing the main points of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment in an easy-to-understand format.
Historical Context of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Tracing the Autoimmune Disease
Our final thoughts on rheumatoid arthritis emphasize the imperative of empowering both patients and healthcare professionals in the ongoing battle against this chronic autoimmune disease. For patients, empowerment comes from comprehensive education, active participation in treatment decisions, and access to supportive resources that foster resilience and self-management skills. Understanding the nuances of their symptoms, the role of their immune system, and the importance of adherence to treatments is fundamental. For healthcare professionals, empowerment stems from continuous professional development, access to the latest research and clinical tools, and fostering a patient-centered approach. By strengthening this collaborative dynamic, we can collectively enhance diagnostic accuracy, optimize treatment outcomes, and significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with rheumatoid arthritis, moving closer to a future where its impact is minimized.
A handshake between a patient and a doctor, symbolizing the collaborative empowerment in managing rheumatoid arthritis.
Current Landscape of Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatments: An Information Deep Dive
Your call to action for effectively managing rheumatoid arthritis involves proactively seeking expert care and embracing continuous education. If you suspect you have rheumatoid arthritis or are experiencing persistent joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, consult a healthcare provider immediately to get an accurate diagnosis. Early intervention by a rheumatologist is crucial to prevent irreversible joint damage. Once diagnosed, commit to your prescribed treatment plan, which will likely involve DMARDs to control the autoimmune response and manage inflammation. Beyond medication, actively educate yourself about the disease: understand its impact on your joints, learn about lifestyle modifications, and engage in physical therapy. Leverage reliable resources and support networks. Taking these decisive steps will empower you to navigate the challenges of rheumatoid arthritis confidently, optimize your health, and strive for the best possible quality of life, demonstrating proactive self-advocacy.
A person looking at a medical pamphlet about rheumatoid arthritis, with a "Call to Action" button highlighted, emphasizing seeking expert care.
Navigating Your Next Steps in Rheumatoid Arthritis Management and Treatment
Navigating your next steps in rheumatoid arthritis management and treatment requires a strategic and informed approach. After initial diagnosis and treatment initiation, regular follow-ups with your rheumatologist are essential to monitor disease activity, assess treatment effectiveness, and make necessary adjustments to your medication regimen. Be proactive in communicating any changes in symptoms, new pain, or concerns about side effects. Consider incorporating complementary therapies, such as acupuncture or massage, only after discussing them with your healthcare provider to ensure they align with your overall treatment plan and do not interfere with prescribed medications. Building a strong support system, including family, friends, and support groups, can provide invaluable emotional and practical assistance. Remember that managing rheumatoid arthritis is a dynamic process, and staying informed and engaged is key to adapting to its evolving challenges and maintaining optimal joint function and quality of life.

A roadmap showing different paths for rheumatoid arthritis management, including follow-ups, therapy, and support networks.
First Steps in Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis: Identifying Key Signs and Symptoms
To further support patients and healthcare professionals, valuable additional resources are available, encompassing clinical tools, cutting-edge research, and comprehensive guidelines for rheumatoid arthritis. Reputable organizations like the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) publish evidence-based guidelines that dictate best practices for diagnosis and treatment. Online clinical tools, such as disease activity calculators and patient-reported outcome measures, assist in monitoring disease progression and treatment efficacy. Access to peer-reviewed research journals keeps professionals updated on the latest scientific breakthroughs, from new drug developments to innovative therapeutic strategies for managing inflammation and pain. For patients, these resources often come in the form of educational brochures, webinars, and patient advocacy group websites that provide clear, actionable information about their condition, symptoms, and the various treatments available to combat the chronic inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis, empowering them to make informed decisions about their care.
A collection of books, journals, and a tablet displaying online clinical tools, representing valuable resources for rheumatoid arthritis.

















